Building a Scalable E-Commerce Platform with Docker Compose and Spring Microservices
Project Overview
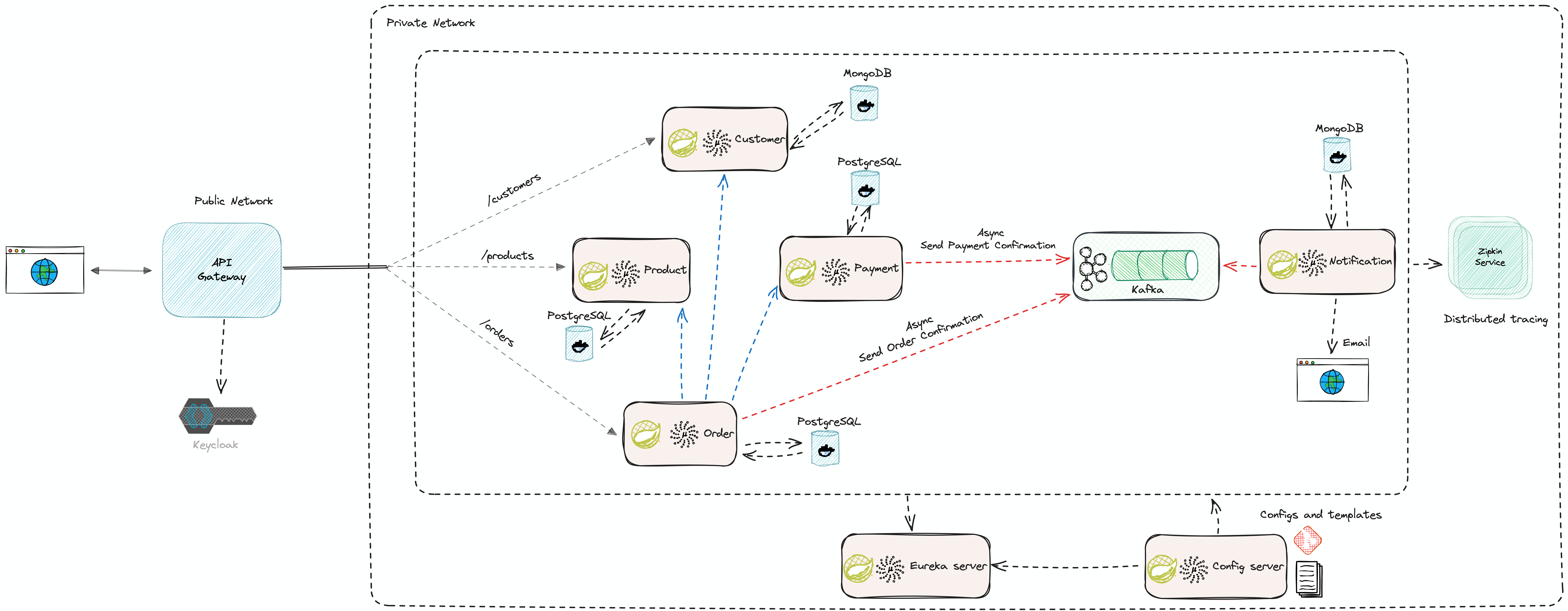
This project demonstrates my implementation of a scalable e-commerce platform using microservices architecture. The solution addresses key challenges in modern e-commerce applications including modular development, independent deployability, and service isolation while maintaining a cohesive system.
Source Code
The complete source code is available on GitHub: E-Commerce Microservices Repository
Core Technologies
The platform is built using the following technologies:
- Java Spring Boot: For microservice implementation
- Spring Cloud Gateway: For API gateway functionality
- Spring Data JPA: For data access layer
- Spring Security: For authentication and authorization
- MySQL: For persistent data storage
- Docker & Docker Compose: For containerization and service orchestration
- Zipkin: For distributed tracing
- Eureka: For service discovery
- Swagger/OpenAPI: For API documentation
Microservices Architecture Implementation
Service Composition
The e-commerce platform is composed of the following microservices:
graph TD
A[API Gateway] --> B[Product Service]
A --> C[Order Service]
A --> D[Inventory Service]
A --> E[Discovery Server]
B -.-> F[(Product DB)]
C -.-> G[(Order DB)]
D -.-> H[(Inventory DB)]
classDef service fill:#4285F4,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
classDef database fill:#34A853,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
classDef infrastructure fill:#FBBC05,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1px,color:white;
class A,B,C,D service;
class F,G,H database;
class E infrastructure;
Each service has a specific business function:
- Product Service: Manages product catalog and information
- Order Service: Handles order creation and processing
- Inventory Service: Manages product stock levels
- API Gateway: Routes client requests to appropriate services
- Discovery Server: Provides service registration and discovery
API Gateway Implementation
The API Gateway serves as the single entry point for all clients, implemented using Spring Cloud Gateway:
- Routing: Routes requests to the appropriate microservices based on path
- Load Balancing: Client-side load balancing for distributed instances
- Integration with Discovery Service: Dynamic service resolution
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: product-service
uri: lb://product-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/product/**
- id: order-service
uri: lb://order-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/order/**
- id: inventory-service
uri: lb://inventory-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/inventory/**
Service Discovery with Eureka
The project uses Netflix Eureka for service discovery, allowing services to find and communicate with each other without hardcoded URLs:
- Service Registration: Each microservice registers itself with Eureka
- Service Discovery: Services locate each other through the Eureka server
- Health Monitoring: Automatic detection of service health
This implementation allows for dynamic scaling and replacement of service instances without configuration changes.
Inter-Service Communication
The project implements two communication patterns:
Synchronous Communication (REST)
- Used for immediate responses and direct service-to-service calls
- Example: Checking inventory availability during order placement
WebClient Integration
- Non-blocking HTTP requests between services
- Example: Order service communicating with inventory service
// Example of WebClient usage in Order Service
private final WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder;
public OrderService(WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder) {
this.webClientBuilder = webClientBuilder;
}
private Boolean checkInventory(String skuCode) {
return webClientBuilder.build().get()
.uri("http://inventory-service/api/inventory/" + skuCode)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Boolean.class)
.block();
}
Data Management Strategy
Each microservice has its own dedicated database:
- Product Service Database: Stores product information
- Order Service Database: Manages order data
- Inventory Service Database: Tracks product inventory levels
This approach provides:
- Decoupling: Changes to one service’s data model don’t affect others
- Independent Scaling: Database resources can be allocated according to service needs
- Technology Independence: Each service can use the database technology best suited to its requirements
Containerization with Docker Compose
The entire application is containerized using Docker with Docker Compose for orchestration:
# Excerpt from docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
## MySQL Database
mysql:
container_name: mysql
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=mysql
- MYSQL_DATABASE=order-service
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- ./mysql:/var/lib/mysql
healthcheck:
test: "/usr/bin/mysql --user=root --password=mysql --execute \"SHOW DATABASES;\""
interval: 2s
timeout: 20s
retries: 10
## Zipkin
zipkin:
image: openzipkin/zipkin
container_name: zipkin
ports:
- "9411:9411"
## Eureka Server
discovery-server:
image: ${DOCKER_USERNAME}/discovery-server:latest
container_name: discovery-server
pull_policy: always
ports:
- "8761:8761"
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=docker
depends_on:
- zipkin
## API Gateway
api-gateway:
image: ${DOCKER_USERNAME}/api-gateway:latest
container_name: api-gateway
pull_policy: always
ports:
- "8181:8080"
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=docker
- LOGGING_LEVEL_ORG_SPRINGFRAMEWORK_SECURITY=TRACE
depends_on:
- zipkin
- discovery-server
## Product Service
product-service:
container_name: product-service
image: ${DOCKER_USERNAME}/product-service:latest
pull_policy: always
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=docker
depends_on:
- mongo
- discovery-server
- api-gateway
## Order Service
order-service:
container_name: order-service
image: ${DOCKER_USERNAME}/order-service:latest
pull_policy: always
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=docker
depends_on:
mysql:
condition: service_healthy
discovery-server:
condition: service_started
api-gateway:
condition: service_started
## Inventory Service
inventory-service:
container_name: inventory-service
image: ${DOCKER_USERNAME}/inventory-service:latest
pull_policy: always
environment:
- SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=docker
depends_on:
mysql:
condition: service_healthy
discovery-server:
condition: service_started
api-gateway:
condition: service_started
Benefits of using Docker Compose:
- Infrastructure as Code: Environment defined in version-controlled files
- Consistency: Identical environments across development and production
- Simplified Deployment: One command to start the entire system
- Dependency Management: Proper service startup order and health checks
Distributed Tracing
The project implements distributed tracing with Zipkin:
- Request Tracking: Trace requests as they travel through multiple services
- Performance Monitoring: Identify bottlenecks and latency issues
- Error Analysis: Track where failures occur in the request chain
This provides valuable insights for debugging and performance optimization in a distributed environment.
Implementation Details by Service
Product Service
The Product Service manages the product catalog, implemented with:
- REST API for CRUD operations on products
- MongoDB for flexible document storage
- Spring Data MongoDB for data access abstraction
Key features:
- Product creation and retrieval
- Product information management
- Catalog organization
Order Service
The Order Service handles order processing with:
- Transaction Management: Ensuring order consistency
- Integration with Inventory: Checking stock availability before order placement
- MySQL Database: Relational storage for order data
- Order Event Generation: Creating events upon order placement
Inventory Service
The Inventory Service manages product stock levels:
- Stock Verification API: Checking if products are in stock
- Inventory Updates: Adjusting stock levels as products are ordered
- MySQL Database: Tracking inventory quantities
CI/CD Pipeline
A key part of the project is the automated build and deployment process:
- GitHub Actions: Automated workflows for testing and building
- Docker Hub Integration: Publishing container images
- Automated Testing: Running tests before deployment
Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Service Discovery in a Containerized Environment
Solution: Implemented Eureka service discovery with Docker-specific configuration to handle network isolation.
Challenge 2: Database Initialization and Migration
Solution: Used Flyway for database schema migration, ensuring consistent database initialization across environments.
Challenge 3: Inter-Service Communication Reliability
Solution: Implemented proper error handling and circuit breakers for service-to-service communications to prevent cascading failures.
Challenge 4: Container Orchestration
Solution: Created a well-structured Docker Compose file with health checks and dependency management to ensure proper service startup order.
Lessons Learned
Building this microservices-based e-commerce platform provided valuable insights:
- Service Boundaries: Defining clear service boundaries based on business capabilities is crucial
- Configuration Management: Externalizing configuration for different environments simplifies deployment
- Docker Compose Benefits: Docker Compose provides a good balance of simplicity and power for small to medium microservices deployments
- Observability Importance: Implementing proper logging and tracing from the start saves significant debugging time
- Start Small: Begin with core services and expand gradually rather than attempting to build everything at once
Conclusion
This e-commerce microservices project demonstrates a practical implementation of microservices architecture using Spring Boot and Docker Compose. The approach provides modularity, independent deployability, and technology diversity while maintaining system cohesion through well-defined interfaces and service discovery.
The Docker Compose orchestration offers a lightweight yet powerful way to manage multiple services without the complexity of full Kubernetes orchestration, making it ideal for small to medium-sized projects or as a stepping stone toward more complex deployments.
The resulting platform provides a solid foundation for an e-commerce business with the flexibility to evolve individual components independently while maintaining overall system integrity.